It’s 4:35 PM Friday.
Anna just got off a Zoom call. The client asked for a timeline and cost estimate and needed it by the end of the day. Anna knows the information exists somewhere: the updated cost structure is in an Excel buried in Teams, the risk report is in her inbox with the team, and the project timeline? That might still be in someone else’s box chat. She sighs, opens six tabs, scrolls through three folders, and pings a colleague:
“Hey, where did you put the final version of the timeline we discussed last week?”
30 minutes pass. The deadline’s looming. Switching between taps, hopping on and off different files… The plan of a weekend spa treatment is going to fall through again.
And Anna is not alone. The state of madness caused by “enterprise knowledge management” problems is indeed a nightmare that most modern enterprise executives are dealing with.
At Verysell AI, we see this story far too often. In fact, Forrester reports employees spend up to 12 hours a week just looking for the information they need to do their jobs. That’s more than a full workday lost in digital clutter every single week!
Fortunately, here’s the good news: This is fixable. And it doesn’t require more folders or stricter protocols, but just smarter tools. That’s where AI-powered Enterprise Knowledge Management comes in.
1. What is EKM?
Enterprise knowledge management (EKM) is a strategic approach to planning, organizing, motivating, storing and controlling of people, processes and systems within an organization, ensuring its knowledge-related assets are effectively utilized to enhance overall efficiency. It entails formally managing knowledge resources to facilitate access and reuse of knowledge, typically by using advanced information technology (D. E. O’Leary, 1998).
It aims at managing knowledge and making it accessible and reusable to any individual in an enterprise, trying to break the never-ending loop of being trapped under a mountain of documents, mystery PDFs, and ‘final_final_really_final_timeline.docx’ files with no escape in sight.
2. Types of knowledge
According to the codification of the information, knowledge can be categorized into three types (IBM, 2021):
- Explicit knowledge: is structured, tangible information captured within document types such as manuals, reports, and guides, allowing organizations to easily share knowledge across teams. This form of knowledge is important to retain intellectual capital within an organization as well as facilitate successful knowledge transfer to new employees. This is probably the most well-known type, also known as “know-what” knowledge
- Implicit knowledge: has yet to be documented. It tends to exist within processes of application of learned (explicit) knowledge, and it can be referred to as “know-how” knowledge (King, 2009)
- Tacit knowledge: is typically acquired through experience and intuition. This type of knowledge, therefore, is challenging to articulate and codify, making it difficult to transfer this information to other individuals. This is the “know-why” knowledge, requiring people to have a deep comprehension of causal relationship, interactive effects and the uncertainty levels associated with observed stimuli or symptoms.
3. AI changes the EKM process
Along four main phases of the process, AI stands as a central enabler of more efficient, dynamic, and intelligent KM processes. AI-powered systems have improved each step of the process by leveraging advanced analytics, Natural Language Processing (NLP), and Machine Learning (ML) to enhance each phase of KM across organizations. At Verysell AI, our service – VeryChat – is built to do that, empowering users todeal with complex data in every stage of EKM process.

Knowledge creation
used to be endless hours of typing, searching, organizing any existing or new information, and praying someone would read the knowledge base. With AI, it is no longer solely dependent on human input. NLP and ML enable platforms to automatically extract insights from emails, meetings, documents, and customer interactions.
VeryChat, for example, with the Web chat function, can assist users to interact and navigate on public websites more easily by summarizing content, or extracting key information from long written texts.
Furthermore, AI can transcribe conversations, summarize threads, and even spots what’s missing, generating structured knowledge bases from unstructured data sources in real time. Basically, it’s like your very own overachieving note-taker who never sleeps.
Knowledge storage and retrieval
This is when information is formatted to meet the requirements of repository and distribution. Instead of dumping files into dusty digital cabinets (aka shared drives no one understands), AI turns storage into a smart, organized brain and searchable platforms.
VeryChat’s Document chat and Sharepoint folder chat are designed to support this stage. Explicit knowledge uploaded by employees from diverse sources is collected and organized within SharePoint, enabling fast, accurate retrieval across the company. All staff can easily store their files at one shared space, making it easy to look back later.
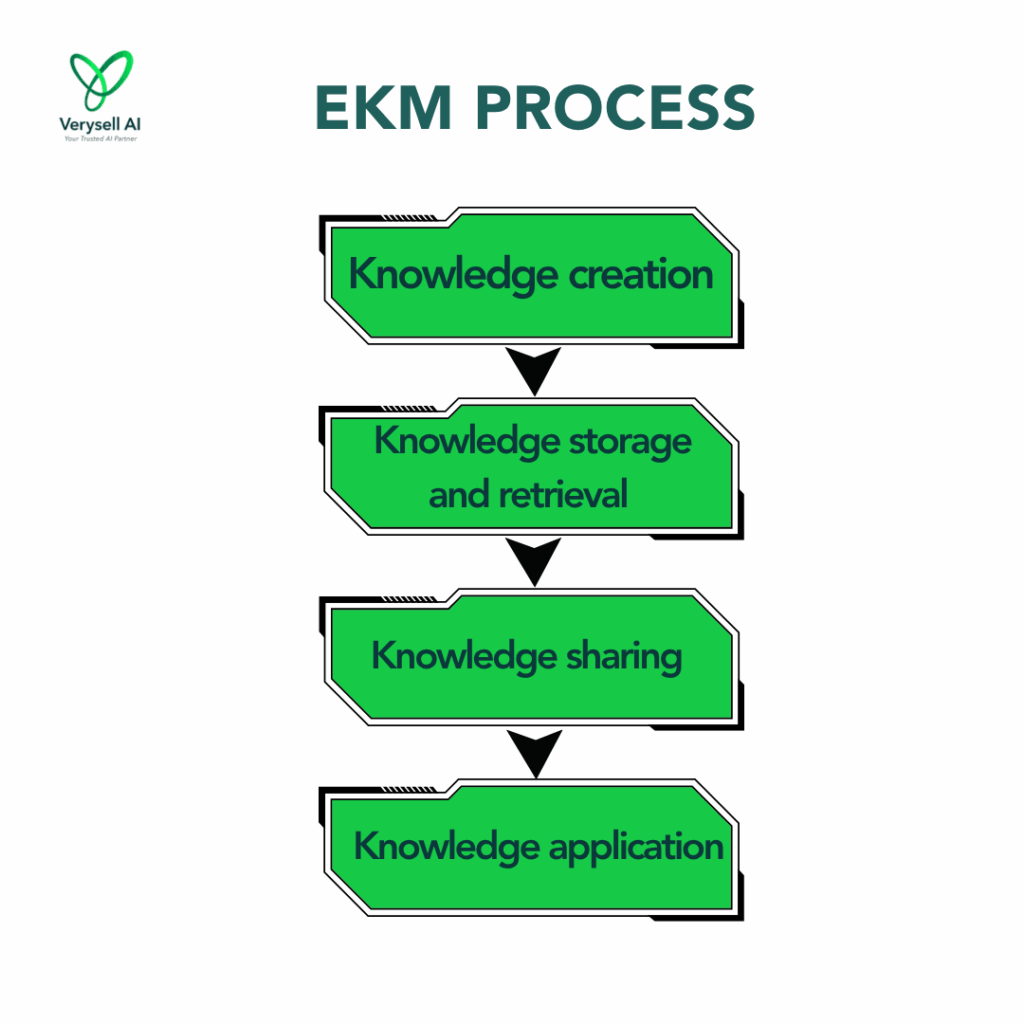
Knowledge sharing
In this stage, knowledge is spreaded broadly across the enterprise. AI helps knowledge flow like a group chat with purpose, enabling real-time collaboration. It connects the right people, at the right time, with the right insights. For instance, AI can facilitate peer feedback on internal platforms or sync insights between marketing and sales in real time, ensuring the right knowledge reaches the right people when it’s needed most.
Knowledge application
This is when insights and information are really used in daily workflows, decision-making, and problem-solving. With AI, information doesn’t just sit in a folder hoping to be found. It shows up when you need it. Tools like voice assistants and smart search help users quickly find and act on relevant information. Bonus: AI makes it socially easy to ask for help. No awkward “Hey, sorry to bother you, but do you have that thing?”. Just type or ask, and AI delivers with zero judgment, 24/7 support.
4. The Bottleneck: Growing crisis in EKM
The integration of AI and EKM opens complex challenges for modern organizations. As enterprises adopt AI to strengthen their KM practices, they must navigate a nuanced landscape filled with technological, ethical, and operational considerations that demand thoughtful analysis (Rezaei, 2025).
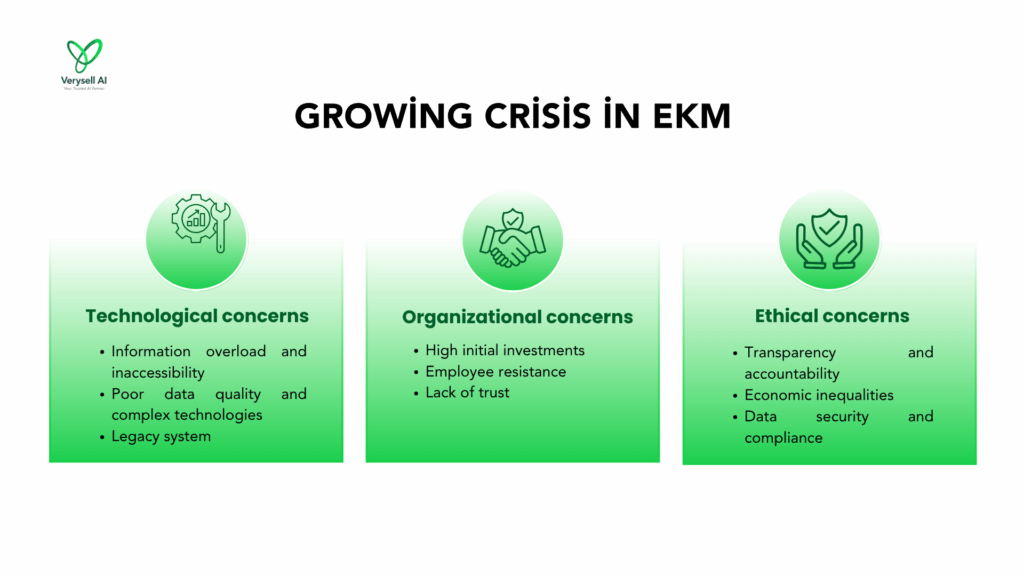
4.1. Technological concerns
Technological challenges remain a significant barrier to effective AI-powered KM. One key issue is information overload and inaccessibility. According to a Forrester study, employees reported losing nearly 12 hours per week searching for data hidden in silos. Many businesses have to deal with the problem that their data is currently stored in different formats, in disparate datasets, and sometimes still on paper, which is not for AI integration. The disperse of information across various platforms make it more challenging for workers to navigate, learn and apply effectively.
In addition, scaling AI tools presents serious obstacles, with 75% of organizations struggling to adopt AI effectively because of poor data quality and overly complex technologies (Deloitte, 2024). Employes with low technical skills might be overwhelmed with the complication of new AI tools. These issues not only hinder productivity but also limit the full potential of AI in supporting seamless knowledge access and application.
Another major challenge is integrating AI with existing legacy systems. Many organizations still rely on former KM platforms that were not built to work smoothly with modern AI technologies. Combining these systems often requires extensive resources, specialized skills, and considerable adjustments to current workflows, making the process both time-consuming and expensive.
4.2. Organizational concerns
One primary challenge of AI deployment is high investment required. According to S&P Global’s 2023 Global Trends in AI report, over half of AI decision-makers in leading enterprises with over 250 employees report that cost remains a major barrier to adopting the latest AI tools. Obviously, even well-resourced firms struggle with the financial demands of cutting-edge AI implementation.
In addition, employees’ resistance to change is another organisational hurdle. This is ascribed to the technological challenges: employees’ lack of technical skills and unexplained complex tools. Such resistance can be worsened if workers do not trust AI, particularly when their decision-making processes lack transparency or appear to contradict human intuition (Siau and Wang, 2020). Implementing AI-based KM systems often necessitates detailed education and training to employees, and comprehensive alterations to existing processes and workflows.
4.3. Ethical concerns
One key ethical issue is transparency and accountability. Many AI systems function as “black boxes,” making it difficult to understand how decisions are made or to trace the reasoning behind specific outputs. This lack of clarity can undermine trust and accountability within organizations. Furthermore, when AI systems make errors or produce biased outcomes, it’s often unclear who is responsible, the developers, the users, or the system itself. This ambiguity complicates both internal governance and external regulatory compliance.
The economic impact of AI, particularly in the form of job displacement, raises questions about fairness and social responsibility. Without thoughtful planning, AI implementation may widen economic inequalities by replacing human roles without adequate reskilling or job transition support.
Finally, data security and compliance remain pressing ethical risks. According to IDC (2024), 77% of enterprises lack unified data governance for AI, leaving them vulnerable to data breaches, legal penalties, and reputational harm. Ensuring strong governance frameworks is essential to ethically managing AI-driven knowledge systems.
5. How AI is Rewriting EKM
5.1. Intelligent Search and Retrieval
Traditional search is being replaced by AI-powered, conversational experiences. Natural language processing (NLP) enables users to ask natural, plain language questions and receive precise, context-aware answers. Employees can query PDFs or Word files to extract details or summaries.
For example, a compliance officer can instantly retrieve the latest regulatory guidelines or audit checklists, while a project manager can access up-to-date timelines or risk assessments without combing through multiple folders. The integration of chat-based interfaces with enterprise-grade systems ensures that knowledge is not only accessible but also secure and permission-aware. By understanding user intent, these systems surface highly relevant information across platforms like SharePoint, Teams, Notion, or email systems.
5.2. Automated Question Answering
Beyond traditional search, AI enables real-time, accurate responses to user queries by drawing from multiple knowledge sources, including wikis, document repositories, and databases. Techniques like Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) reduce the risk of misinformation and ensure that responses remain grounded in verified content. AI-driven chatbots and virtual assistants, using NLP, can quickly interpret and respond to user questions with precision, reducing the need for manual searches and boosting productivity.
VeryChat has performed these functions effectively with its Document Chat, Web Chat, and Database Chat. Instead of simple searching for location of a file by keywords, users can use questions to extract needed piece information, summarize long text, or ask for insights generated from documents. From stored knowledge, VeryChat can provide users with reports, charts and graphs from clean data source provided. This efficient communication approach improves both workflow speed and user satisfaction in EKM systems.
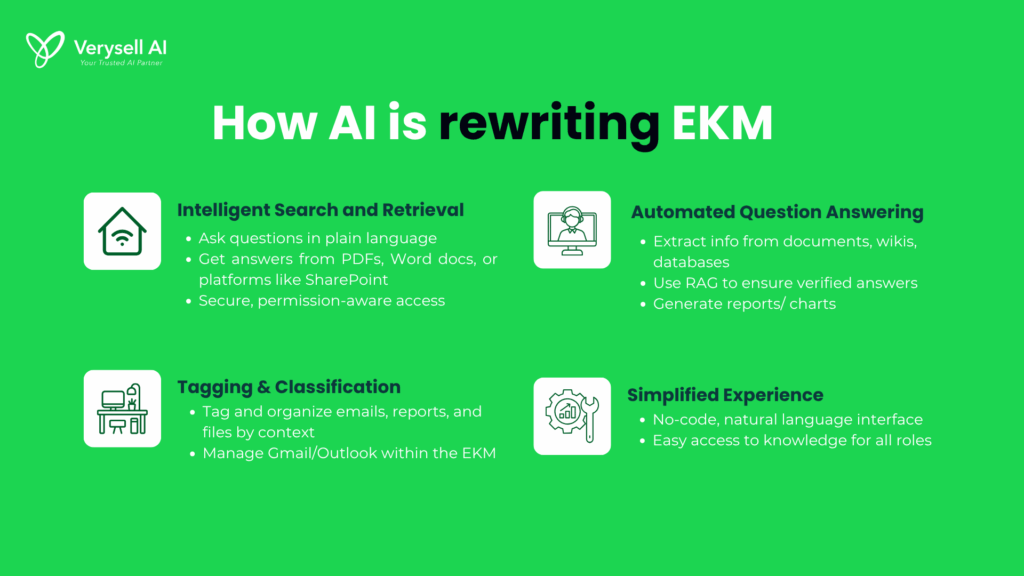
5.3. Content Tagging and Classification
Enterprises generate vast amounts of unstructured data daily, from emails and reports to presentations and project files. AI helps streamline this complexity by automatically tagging and classifying content based on context, themes, or usage. This capability significantly reduces manual effort, improves searchability, and ensures that relevant knowledge can be retrieved precisely when needed. Email threads related to customer feedback can be categorized by product line or urgency, while uploaded documents are sorted by function or department. VeryChat’s Mailbox Chat function can integrate email systems like Gmail or Outlook. Therefore, users can query, better manage and send emails through the EKM system.
5.4. Simplified Experience
One of the biggest breakthroughs in modern EKM is bridging the gap between complex systems and everyday users, minimizing employee resistance. AI services like VeryChat are designed to do exactly that. A no-code, natural language interface lets teams engage with data, documents, and workflows by simply asking questions without IT support, no technical manuals, no learning curve:
- Democratized access to knowledge without the need for coding skills
- Secure, role-based permissions so only the right eyes see the right data
- API integrations to sync with CRM, ERP, and other systems in the background, so knowledge always stays fresh and relevant
By simplifying the interface and supercharging the backend, VeryChat makes enterprise knowledge more usable for everyone, whether you’re in legal, sales, or customer support.
The future of EKM is smarter. Will you catch up or lead?
AI is not simply enhancing existing EKM practices, it’s rewriting them.
For people like Anna, it means no more wasting hours chasing down documents, pinging five people for the same answer, or digging through dusty folders. With secure integrations, permission-aware automation, and intuitive interfaces, AI enables a more connected, simplified, intelligent, and accessible knowledge environment for modern enterprises.
Still stuck asking “Where’s that file?” every day? Let us show you a better way. Email or call us for a quick VeryChat demo and discover how effortless enterprise knowledge management can be.


