Generative AI has moved beyond hype into practical, high-impact applications for industries that rely on efficiency, precision, and scale (Prather et al., 2024). Manufacturing and supply chains are prime candidates. With global supply chains facing disruption, rising costs, and demands for sustainability, the adoption of AI-driven tools can redefine how factories design products, optimize operations, and deliver value. This blog post explores the top 5 generative AI applications in manufacturing and supply chains, examining how they address key challenges while unlocking new opportunities for innovation, speed, and cost efficiency.
>> Click here to identify top 6 AI-powered forecasting to optimize supply chain efficiency
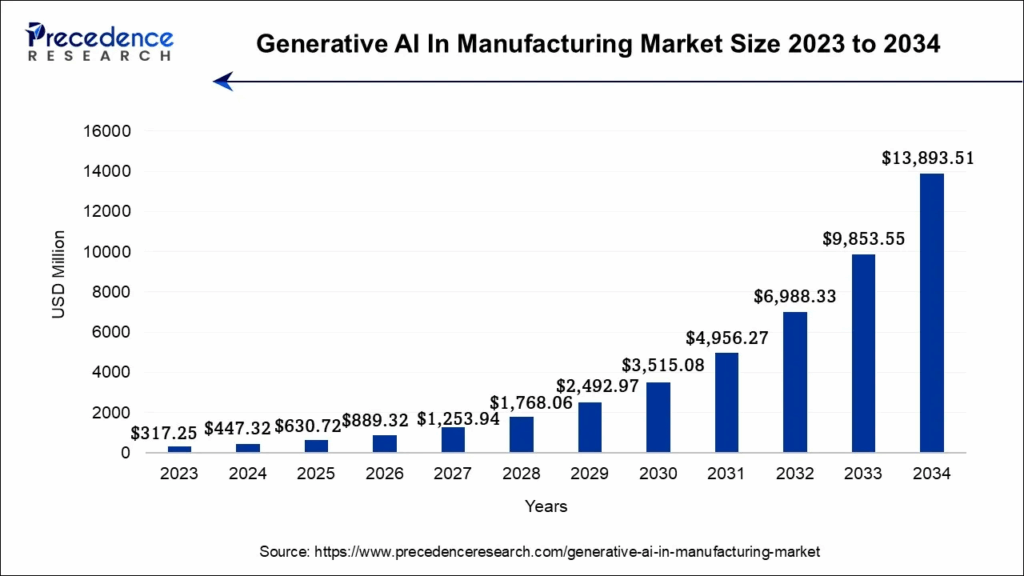
1. Generative AI In Manufacturing Market Size
According to Precedence Research (2025), the global market for generative AI in manufacturing is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 41% from 2024 to 2034, from an estimated USD 447.32 million in 2024 to around USD 13,893.51 million by 2034.
Generative AI models and applications like ChatGPT are utilized in the industrial sector to generate text automatically in order to assist operations. Additionally, generative AI may assist by transforming words into codes or graphics, enabling businesses to improve their manufacturing process. Manufacturers are working to speed up production processes in response to increased product demand and commercialization, which is driving growth in the worldwide generative AI manufacturing market.
2. AI in Supply Chain Optimization
Overview: Generative AI accelerates the design cycle by creating, testing, and refining product concepts in real time. Engineers can input constraints such as weight, material, or performance requirements and AI generates multiple optimized designs.
Impact:
- Reduces prototyping costs by 30–50%
- Shortens design cycles from months to weeks
- Expands innovation by suggesting non-intuitive geometries
Example: Airbus has leveraged AI to generate lightweight aircraft components, cutting fuel consumption without compromising safety (Airbus, 2025). Similarly, automotive manufacturers use AI-driven generative design to experiment with sustainable materials and aerodynamic structures.
3. Predictive Maintenance and Smart Operations
Overview: Traditionally, maintenance followed either a fixed schedule or a reactive model, waiting for equipment to fail. Generative AI flips this approach. By analyzing sensor data, AI creates predictive models that not only forecast when machines might fail but also simulate repair scenarios to minimize downtime.
Impact
- Increases equipment uptime by up to 20%
- Cuts maintenance costs by 10–15%
- Improves worker safety by preventing unexpected breakdowns
Example: Siemens uses AI algorithms within its “MindSphere” platform to monitor turbines and manufacturing lines, recommending the most efficient maintenance windows (Business 2.0, 2025). This proactive approach minimizes disruptions across complex global operations.
4. Supply Chain Simulation and Risk Management
Overview: Supply chains are increasingly vulnerable to geopolitical tensions, climate risks, and shifting consumer demand. Generative AI can simulate countless “what-if” scenarios, helping managers stress-test supply chain resilience. By generating models of alternative supplier networks, transport routes, and demand shifts, AI equips leaders with actionable strategies before crises occur.
Impact
- Reduces risk exposure by modeling disruptions in advance
- Optimizes logistics costs by 15–20%
- Enhances resilience through alternative sourcing pathways
Example: DHL has piloted AI-based scenario planning to forecast delays caused by port congestion or extreme weather, enabling rerouting before issues escalate.
5. AI-Driven Quality Control and Defect Detection
Overview: Quality control has long relied on human inspection or rule-based vision systems. Generative AI goes further: it learns from large datasets of “good” and “defective” products, generating new representations of possible defects that may not yet exist in training data. This anticipatory ability enhances accuracy and reduces false negatives.
Impact
- Boosts defect detection accuracy to above 95%
- Reduces waste by up to 40%
- Cuts recall costs significantly
Example: Electronics manufacturers now employ AI-powered vision systems that detect microscopic soldering defects invisible to the human eye, ensuring higher product reliability in sensitive industries like semiconductors and medical devices.
6. Personalized Customer Demand Forecasting
Overview: Forecasting demand has always been a complex balancing act between inventory efficiency and service reliability. Generative AI enhances forecasting by simulating demand variations at granular levels per customer segment, per region, even per SKU. These models help businesses avoid both stockouts and overproduction.
Impact
- Improves forecast accuracy by 20–30%
- Lowers inventory holding costs by up to 25%
- Enables dynamic production planning aligned with real demand
Example
Unilever has integrated AI-driven demand forecasting into its supply chain, helping synchronize production with regional consumer behavior, reducing waste, and supporting sustainability goals.
Future Outlook
Generative AI in manufacturing and supply chains is still evolving, with future developments pointing toward even greater transformation. We can anticipate the rise of autonomous factories, where AI-driven systems dynamically adjust production lines in real time to maximize efficiency and flexibility. At the same time, closed-loop sustainability will become a reality as AI optimizes recycling, reuse, and circular supply chain models to reduce waste and environmental impact. Rather than replacing human expertise, collaborative AI will increasingly support and enhance creativity and decision-making across the value chain. Together, these advancements signal a trajectory toward smarter, greener, and more resilient global supply networks.
Conclusion
Generative AI is reshaping manufacturing and supply chains in ways once considered futuristic. From design to delivery, it drives cost savings, agility, and innovation. By adopting AI in these five key areas—product design, predictive maintenance, supply chain risk modeling, quality control, and demand forecasting—companies can gain a competitive edge in a volatile global market.
Manufacturers that embrace AI not only strengthen their operational resilience but also align with the broader push toward sustainability, customer-centricity, and efficiency. In short, generative AI is not just a tool—it’s a catalyst for the next industrial revolution.


