Autonomous AI is reshaping how organizations operate, enabling systems that don’t merely assist humans but independently observe, decide, and act in pursuit of strategic goals. In this new paradigm, enterprises no longer rely solely on reactive AI tools; instead they evolve toward self-governing, goal-oriented systems capable of driving operational excellence at scale.

This evolution carries significant implications for how businesses manage workflows, governance, risk, and strategic decision-making. As adoption accelerates, understanding the core drivers behind this transformation is essential for executives and technology leaders
>> Click here to deeply understand how 10 critical ways of AI in automative industry!
Deloitte predicts that by 2025, 25% of companies using GenAI will pilot such autonomous agents, doubling to 50% by 2027. This reflects a strong desire to scale and gain greater control over the governance of these new technologies.
1. Beyond Assistance: The Rise of Autonomous AI
Historically, enterprise AI implementations centered on automation and augmentation, systems that either automated repetitive tasks or provided insights that humans acted upon. Autonomous AI represents a strategic leap beyond automation: it delivers orchestrated decisions and adaptive actions across systems and workflows without constant human direction. This shift reflects a broader industry trend towards embedding AI deeply into core operational functions, with capabilities that resemble independent reasoning rather than scripted automation.
By effectively blending data, context, and business logic, autonomous AI systems enable enterprises to operate with increased agility and precision. Instead of generating outputs in response to prompts, these systems continuously monitor environments, interpret complex signals, and execute multi-step actions aligned with organizational goals.
2. What Distinguishes Autonomous AI from Traditional AI Models
To fully appreciate the transformative impact, it is important to clarify how autonomous AI differs from conventional AI and automation:
- Automation vs. autonomy: Automation executes predefined tasks; autonomy orchestrates decisions across systems, adapting to dynamic context.
- Reactive vs. proactive behavior: Traditional AI responds to inputs; autonomous AI anticipates needs and initiates actions toward objectives.
- Rule-based vs. strategic decisioning: Autonomous AI integrates goals, constraints, and evolving context into a decision framework, enabling systems to correct course without manual intervention.
This evolution blurs the lines between intelligence and action, enabling enterprises to streamline operations while elevating strategic responsiveness.
3. Key Enterprise Use Cases
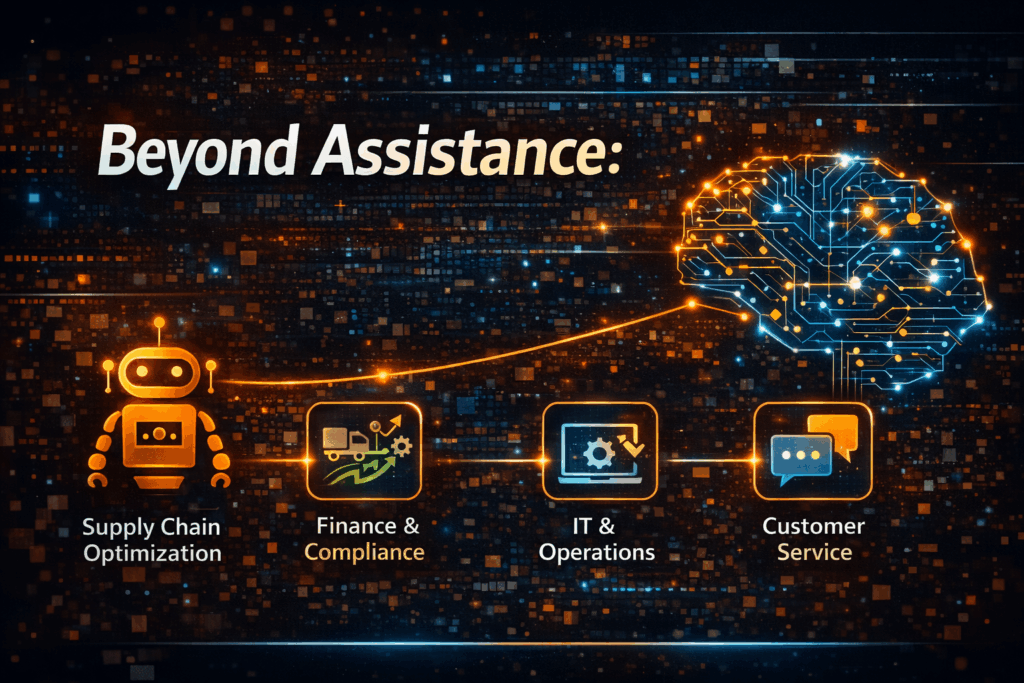
3.1 Supply Chain Optimization
In complex supply chains, autonomous AI can monitor real-time demand, inventory levels, logistics constraints, and external disruptions to automatically adjust routing, replenish inventory, or balance capacity. Rather than relying on static rules or periodic planning cycles, autonomous agents continuously update strategies based on live data, improving resilience and cost efficiency. This independence transforms supply chain operations from reactive to predictive and agile.
3.2 Finance and Compliance
Autonomous AI systems can execute financial workflows such as reconciliation, fraud detection, and compliance verification with continuous auditability and reduced error rates. Because these systems operate with structured logic and traceable decisions, they support accuracy, transparency, and regulatory confidence that is critical in highly regulated environments like banking and insurance.
3.3 IT and Operations
Enterprise AI agents can manage IT helpdesks, system monitoring, and incident resolution autonomously. For example, they can detect anomalies, apply corrective actions, and escalate issues based on predefined risk frameworks—reducing mean time to resolution while liberating human engineers for complex tasks.
3.4 Customer Service
Autonomous customer service AI can not only respond to inquiries but also triage issues, coordinate solutions across departments, and escalate complex cases with context. This extends beyond scripted responses, delivering personalized, proactive engagement at scale with minimal human supervision.
4. Strategic Benefits of Enterprise Autonomous AI
The adoption of autonomous AI delivers a range of strategic advantages that extend beyond incremental efficiency gains:
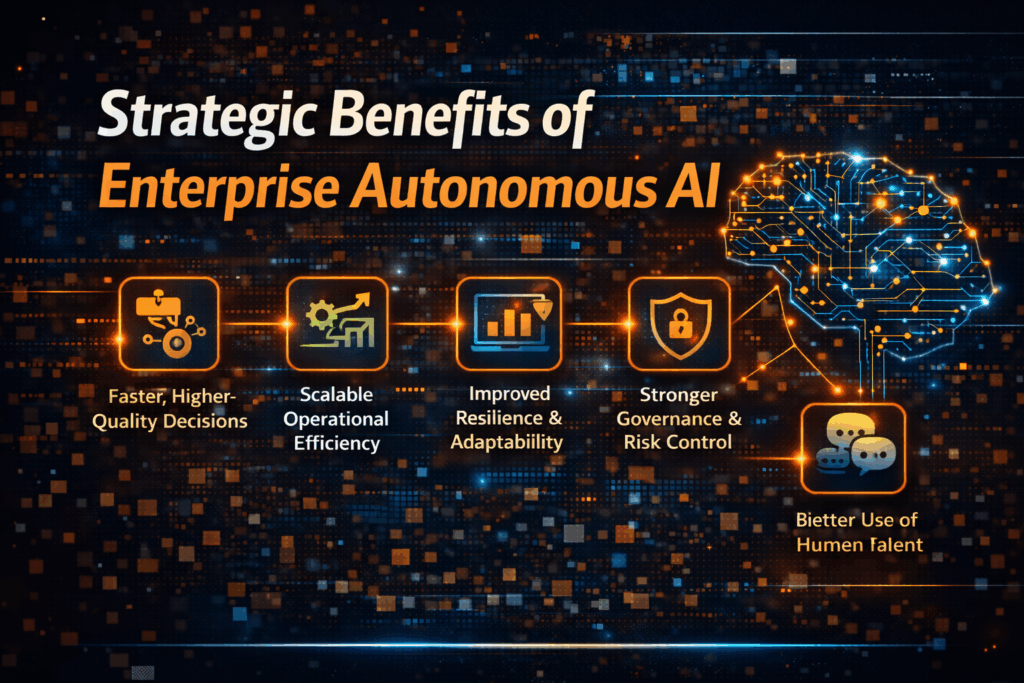
4.1 Enhanced Operational Agility
Autonomous systems adjust to changing business conditions in real time. By continuously analyzing data and adapting actions, enterprises reduce decision latency and enhance responsiveness to market shifts.
By orchestrating end-to-end workflows rather than isolated tasks, autonomous AI lowers marginal operating costs as scope expands. Reusable agents, shared data pipelines, and centralized monitoring enable scale without linear increases in headcount or complexity.
4.2 Scalable Decision-making
Unlike traditional automation, which scales linearly with effort, autonomy enables exponential scaling by establishing reusable, decision-oriented patterns that operate across departments and workflows.
Autonomous systems continuously sense data, evaluate trade-offs, and act within defined objectives. This reduces decision latency and improves consistency across functions, particularly in environments where speed and accuracy directly affect revenue, risk, or customer experience.
4.3 Improved Compliance and Risk Management
Because autonomous AI decisions are deterministic and auditable, enterprises can enforce compliance consistently across processes. This transparency not only increases reliability but also strengthens governance frameworks required in regulated industries.
When designed with guardrails, autonomous AI enforces policies consistently and produces auditable decision trails. Early integration of governance improves regulatory confidence, shortens approval cycles, and reduces operational risk at scale.
4.4 Employee Enablement
By offloading routine and high-volume tasks to autonomous systems, employees can focus on strategic initiatives, innovation, and relationship management that areas where human judgment uniquely adds value.
5. Technical Foundations of Enterprise Autonomy
Achieving effective autonomous operations requires several technological underpinnings:
- Governance and safety guardrails: Structuring boundaries and oversight mechanisms ensures responsible deployment and mitigates risks such as bias or unintended actions.
- Data infrastructure: Autonomous AI depends on high-quality, integrated data sources that provide real-time context for decisioning.
- Persistent contextual memory: Unlike prompt-based models, autonomous systems maintain continuity across interactions and workflows, enabling decisions informed by historical and contextual knowledge.
- Explainable frameworks: To foster trust and compliance, autonomous decisions must be traceable, interpretable, and auditable.
6. Challenges and Considerations
While the promise of autonomous enterprise AI is compelling, adoption is not without challenges:
- Integration complexity: Melding autonomous systems with existing enterprise architecture requires careful planning, especially when integrating with legacy databases, ERP systems, and compliance infrastructures.
- Data governance and security: Autonomous AI requires robust data governance to ensure quality, privacy, and security. Inadequate controls can introduce risk, especially when systems make decisions that cross organizational boundaries.
- Cultural and organizational readiness: Shifting from traditional processes to autonomous operations requires not only technological investment but organizational readiness to trust and adopt AI decisions. Successful implementations include education, governance practices, and change management.
- Risk of over-automation: While autonomy delivers scale, unchecked autonomy without appropriate guardrails can lead to unintended behaviors. Balanced approaches, combining autonomous decisioning with human oversight where necessary, are key to responsible deployment.
7. Best Practices for Scaling Autonomous AI
Enterprises that successfully leverage autonomous AI often follow these guiding principles:
1. Align autonomy with strategic outcomes
Before adoption, define clear business objectives and measurable outcomes to ensure systems are tuned for value rather than experimentation.
2. Build explainable and traceable models
Prioritize transparency in decision logic to strengthen trust across users and regulators.
3. Invest in data readiness
Foundation level data quality, integration, and governance accelerate autonomous decisioning and improve reliability.
4. Establish governance frameworks early
Embed risk management, compliance, and ethical guidelines into operating models to accelerate scaling and reduce friction.
5. Empower cross-functional collaboration
Break silos between business units, IT, and data teams to facilitate smooth adoption and shared accountability for autonomous outcomes.
Conclusion
Autonomous AI marks a pivotal evolution in enterprise technology. Far from incremental automation, it offers enterprises the ability to orchestrate decisions, streamline operations, and accelerate strategic outcomes across departments. As organizations navigate complex markets and mounting operational demands, autonomous AI provides a pathway toward resilient, adaptive, and efficient operations.
While challenges remain particularly in governance, integration, and organizational readiness, enterprises that embrace autonomy with deliberate planning can unlock long-term value and competitive differentiation. The future of enterprise operations is not merely automated that it is autonomous.