AI in BFSI is reshaping the financial landscape, empowering banks, insurers, and fintech firms to operate smarter, faster, and more securely. By integrating AI technologies such as machine learning, predictive analytics, and natural language processing, institutions can enhance decision-making, personalize customer experiences, and strengthen risk management frameworks.
In this guide, we walk you through five actionable steps to effectively implement AI use cases in the BFSI sector from assessing readiness and identifying high-impact use cases to deploying scalable models and ensuring ethical compliance. Whether you’re in banking, insurance, or investment management, these insights will help you turn AI into a sustainable competitive advantage.
>> Click here to deeply understand about AI in BFSI with 9 breakthrough applications!
1. Assess Organizational Readiness
Before implementing AI, institutions must evaluate their digital maturity and data infrastructure. This step sets the foundation for success. Key considerations for implementing AI in financial services revolve around data quality and accessibility (Adeoye et al., 2024). Financial data often resides in silos across various systems, including core banking systems, CRM platforms, loan systems, and legacy applications (Singh, 2025). To harness the full potential of AI, a unified data strategy is crucial. This strategy should facilitate a clean, labeled, and real-time flow of data, breaking down barriers between disparate sources to ensure that decision-makers have access to accurate and timely information (Mainul et al., 2025).
In addition to data considerations, the technology infrastructure plays a vital role in supporting AI initiatives. Organizations must assess their cloud environments, APIs, and data pipelines to determine if they can handle large-scale machine learning workloads effectively (Rella, 2022). Leveraging cloud-based AI platforms such as AWS SageMaker, Azure ML, or Google Vertex AI can offer scalable infrastructure and frameworks that are compliant with regulatory standards. Furthermore, establishing an AI competency center that integrates data scientists, business analysts, and compliance officers is essential for fostering cross-functional alignment and ensuring that AI use cases align with business objectives and compliance requirements (Chauhan, 2024).
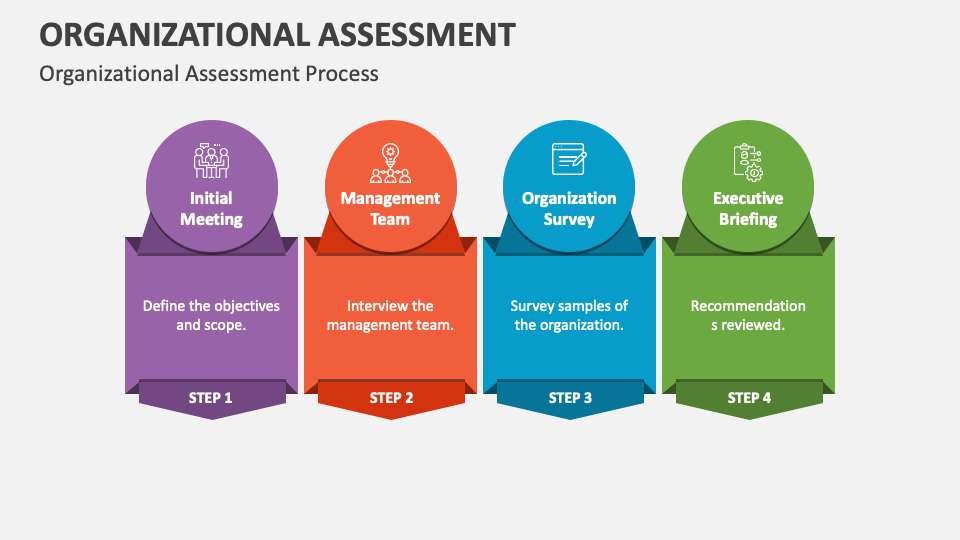
To do organizational assessement process, it has 4 steps from inital meeting, management team, organization survey, and executive briefing. Step 1 is to define the objectives and scope, after that interview the management team for step 2, then do the survey samples of the organisations and step 4 for recommenation reviewed. For example, a mid-sized bank in Southeast Asia launched an internal “AI Readiness Audit” covering data, talent, and infrastructure. The results helped identify outdated systems that hindered model deployment, saving the institution millions in failed pilot costs.
2. Identify High-Impact AI in BFSI Use Cases
Once the foundation is set, the next step is prioritizing areas where AI delivers maximum ROI. In the BFSI sector, AI applications are abundant, but not all are equally valuable or feasible.
2.1 Banking
In the banking sector, high-impact areas include credit scoring, loan approvals, and customer churn prediction (Thenmozhi et al., 2025). These applications leverage advanced predictive analytics and machine learning to assess risk and streamline processes. By implementing these technologies, banks can make faster decisions and improve customer retention. Ultimately, this enhances overall operational efficiency and competitiveness in the market.

2.2 Insurance
For the insurance industry, key applications involve claims automation, underwriting optimization, and fraud detection. Utilizing data-driven insights allows insurers to reduce processing times and mitigate fraud losses effectively. This not only improves operational efficiency but also enhances the customer experience by speeding up claims processing. Consequently, insurers can maintain profitability while delivering a higher level of service.

2.3 Wealth Management
In wealth management, technologies like robo-advisors, portfolio risk modeling, and personalized recommendations play a pivotal role. These tools enable financial institutions to provide tailored investment strategies and manage assets more effectively. By enhancing customer experience and offering personalized services, firms can attract and retain higher-value clients. This ultimately leads to increased assets under management and improved financial performance.

2.4 Customer Service
In the realm of customer service, high-impact applications include AI chatbots, voice assistants, and emotion detection systems. These technologies provide 24/7 support and facilitate quicker responses to customer inquiries, significantly improving satisfaction levels. By automating routine tasks, organizations can free up human agents to focus on more complex issues. This not only enhances service efficiency but also fosters a better overall experience for customers.

When choosing a use case, weigh feasibility (data availability, regulatory compliance, cost) against impact (revenue growth, cost reduction, customer experience). Start small, prove value, and expand. For instance, a regional insurer used natural language processing (NLP) to automate claim form reviews, cutting manual review time by 60% while improving accuracy.
3. Build Scalable Data and Model Architecture
AI implementation in BFSI requires an enterprise-grade architecture that supports scalability, compliance, and transparency (Vajpayee et al., 2024). A scalable architecture for machine learning relies on several core components that facilitate efficient data management and model deployment. A data lake or data warehouse serves as the foundation, centralizing both structured and unstructured data, which is essential for training and inference processes (Nambiar and Mundra, 2022).
This centralized repository allows organizations to store vast amounts of data, ensuring easy access and scalability as data volumes grow. Additionally, a feature store plays a crucial role in managing reusable features across multiple models, promoting consistency and reducing redundancy. By providing a systematic way to store, update, and share features, the feature store enhances collaboration among data scientists and streamlines the model development process.
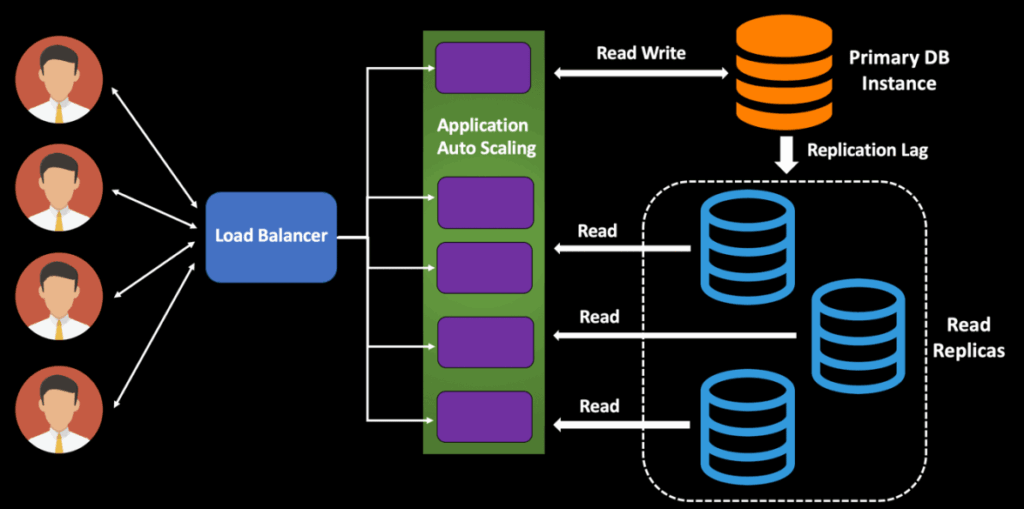
Equally important is the implementation of model lifecycle management through ML Ops, which leverages Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipelines. These pipelines automate the processes of model training, deployment, and versioning, ensuring that models can be updated and rolled back seamlessly as requirements evolve.
Furthermore, integrating explainability and monitoring frameworks is vital to meet regulatory standards, such as the EU’s AI Act or Vietnam’s cybersecurity law. Explainable AI (XAI) frameworks provide transparency into model decisions, enhancing trust and compliance while monitoring systems ensure ongoing performance and ethical use. Together, these components create a robust and scalable architecture that supports the growing demands of machine learning applications in a regulated environment.
Security and compliance are critical. Encryption (at rest and in transit), access control, and audit trails must be non-negotiable. Financial institutions must ensure AI decisions can be explained to auditors, regulators, and customers alike. Take a global bank as an example, it deployed its credit risk models on AWS using an ML Ops pipeline integrated with audit logs. This ensured every model version was traceable, meeting compliance requirements while maintaining agility.
4. Ensure Human-AI Collaboration and Ethical Governance
AI is not meant to replace humans but to augment decision-making. However, without robust ethical governance, it can expose financial institutions to bias, discrimination, and reputational risks.Establishing essential governance practices is crucial for organizations aiming to implement responsible AI in their operations. An ethical framework serves as the foundation, clearly defining what responsible AI means within the context of the organization (Papagiannidis et al., 2025).
This framework should emphasize key principles such as fairness in credit decisions and transparency in automated claims rejection, ensuring that AI systems operate without discrimination and uphold ethical standards. By articulating these values, organizations can create a culture of accountability and trust, both internally and with external stakeholders.
Model explainability is another vital governance practice, as it ensures that users and regulators can comprehend the rationale behind AI decisions. Providing clear and understandable explanations fosters transparency and enhances stakeholder confidence in AI systems. Additionally, ongoing bias detection is essential to identify and mitigate any gender, racial, or socioeconomic biases that may arise in model predictions.
To further strengthen governance, organizations should establish an AI ethics board or integrate AI governance into existing risk management frameworks. This oversight mechanism not only ensures compliance with ethical standards but also promotes a proactive approach to managing the potential risks associated with technologies for AI use cases, ultimately leading to more equitable and responsible AI deployment.
5. Measure, Optimize, and Scale
After successful pilot projects, financial institutions must shift their focus from viewing AI use cases as one-time experiments to embracing them as continuous improvement programs. This transition is vital for maximizing the benefits of AI technologies. To achieve this, organizations should establish clear metrics to track progress and assess the impact of AI on their operations. Key performance indicators include operational efficiency, which measures reductions in manual workloads and processing times; financial performance, which encompasses cost savings, return on investment (ROI), and new revenue streams generated from AI-enabled products; and customer outcomes, as reflected in satisfaction scores, retention rates, and engagement metrics.
In addition to these metrics, monitoring model performance is crucial for ensuring that AI systems deliver reliable and accurate results. Organizations should focus on evaluating accuracy, precision, recall, and drift detection to identify any degradation in model performance over time. Adopting an iterative mindset is essential in this process; feedback loops between operations, analytics, and compliance teams can facilitate the continuous refinement of models. This collaborative approach not only enhances model accuracy but also ensures that the AI systems align with regulatory requirements and operational goals.
Once the AI solutions have proven stable and effective, scaling them across different departments becomes the next logical step. For example, a major ASEAN bank initially deployed AI chatbots for retail customers, resulting in a 40% increase in query resolution speed. Buoyed by this success, the bank expanded its use of AI to other areas, such as loan underwriting and compliance monitoring, within just a year. This strategic scaling not only broadens the impact of AI across the organization but also reinforces a culture of innovation and adaptability, positioning the institution to thrive in an increasingly competitive landscape.