1. Generative AI: Definition and Capabilities
Generative AI refers to artificial intelligence (AI) models that are often based on large language models (LLMs) or transformer architectures. It can generate novel content, such as text, summaries, or structured data, instead of only classifying or predicting. Unlike traditional AI or machine learning, which map inputs to outputs, it can compose, rephrase, summarize, or explain content in fluent, human-like language.
Its core capabilities include:
- Summarization and abstraction: condensing long texts, reports, or documents into coherent summaries
- Content generation: creating drafts of letters, policy documents, claims reports, and narratives
- Paraphrasing, translation, and rewriting: adapting language tone or simplifying technical jargon
- Contextual completion and reasoning: continuing a narrative or filling in logical gaps based on context
- Multimodal synthesis (in advanced models): combining data, images, text, or structured inputs (where available)
In insurance contexts, GenAI becomes particularly powerful because so many workflows depend on text, documents, rules, and regulatory language. By automating or assisting with content tasks, it has the potential to accelerate processes, reduce manual labor, and enhance consistency.
According to EY’s survey, 69% of insurers prefer to invest first in use cases that transform a specific part of the value chain rather than broad adoption at once.
2. How Generative AI Is Transforming Insurance
GenAI is not just an incremental tool. It’s catalyzing a shift in how insurers operate across underwriting, claims, customer engagement, risk, and compliance.
Enabling Efficiency & Automation
Underwriting, claims processing, and policy administration are traditionally labor-intensive. GenAI can reduce the burden of drafting, reviewing, and summarizing documents. As an EY-Gartner joint insight notes, it enabled automation can increase underwriting capacity among employees by reducing time spent on low-level tasks.
Personalization & Customer Experience
Insurers are using GenAI to craft more personalized communications such as explanations of coverage, renewal reminders, or custom policy comparisons. In the health and benefits area, GenAI helps brokers or agents interpret member data and suggest relevant coverage dynamically.
Smarter Risk & Fraud Detection
GenAI models can analyze textual data (claim descriptions, adjuster notes, historical patterns) to surface anomalies and help with fraud detection. It also aids in risk modeling by generating scenario narratives and stress tests. As reported, it is playing a growing role in risk mitigation and claims monitoring. (Michael Shashoua, 2024)
Product Innovation & Marketing
By synthesizing market data, customer segments, and regulatory constraints, GenAI can propose new insurance products or endorsement features. It also helps generate marketing content and campaign drafts tailored to local customer segments.
Transforming the Value Chain
EY suggests that generative AI, combined with predictive analytics and machine learning, is being used to automate application submission, proactively identify risk, and speed claims adjudication, revolutionizing the insurance value chain. Paul Ricard (2025) highlights that leading insurers are aligning AI efforts to real insurance problems, rather than treating AI as a novelty gadget.
Because of these transformations, insurers leveraging the power of generative AI have the opportunity to leap ahead in efficiency, quality, and customer responsiveness.
3. Real-World Use Cases for Insurers
Here are concrete applications of generative AI in insurance, grounded in industry experience and published research.
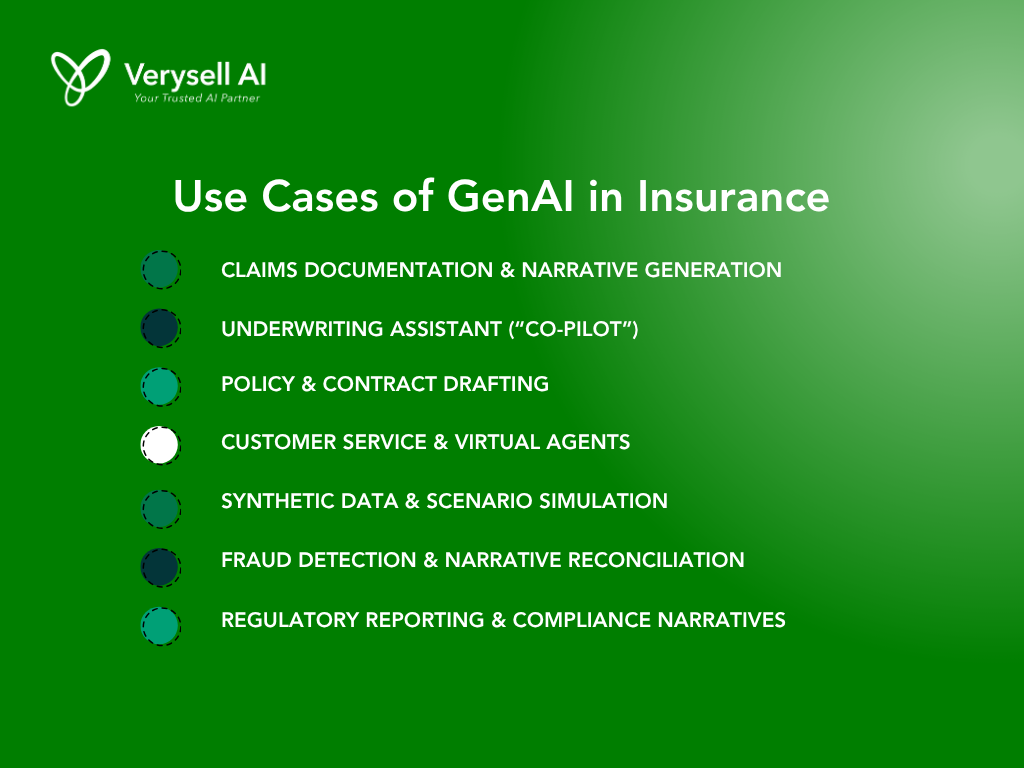
3.1. Claims Documentation & Narrative Generation
When processing claims, insurers must transform raw inputs (photos, reports, surveyor notes) into logic-driven narratives. GenAI can automatically draft coherent claim stories, highlight critical factors, and identify inconsistencies.
3.2. Underwriting Assistant (“Co-pilot”)
An AI assistant can support underwriters by interpreting unstructured data (medical reports, news articles, risk disclosures), drafting risk summaries, and suggesting pricing adjustments. The underwriter reviews and approves final decisions.
3.3. Policy & Contract Drafting
Drafting policy language, riders, or endorsements in multiple jurisdictions is laborious. GenAI can draft initial versions, translate sections, or ensure consistency across documents and regulatory domains. As noted in life insurance discussions, it helps with consistency checking and report drafting.
3.4. Customer Service & Virtual Agents
AI-powered chatbots can answer open-ended questions about policy coverage, claims status, or simplified explanations beyond rigid FAQs. They can respond in a conversational tone and escalate only when needed.
3.5. Synthetic Data & Scenario Simulation
In risk modeling or training, insurers often lack rare-event data. GenAI can create synthetic datasets or simulate future scenarios (e.g., extreme weather, economic shocks) to stress-test models safely.
3.6. Regulatory Reporting & Compliance Narratives
Insurers must compose narrative reports, disclosures, audit commentary, and regulatory filings. Generative AI can draft first-pass versions and flag likely compliance issues, saving legal or compliance teams considerable effort.
3.7. Fraud Detection & Narrative Reconciliation
Generative models can reconstruct alternative claim narratives or compare textual coherence across documents to detect suspicious claims. They assist in anomaly detection by highlighting narrative inconsistencies.
An example from Adam Lewissa mentions a tool (LenAI) that leverages LLMs to streamline claims operations in property & casualty contexts.
4. Three Steps to Help Insurers Get Started
To move from pilot curiosity to strategic deployment, insurers can follow a structured three-step path:
Step 1: Define Strategy & Prioritize Use Cases
Begin with a clear vision: which business challenges (claims speed, underwriting accuracy, customer engagement) offer high ROI if aided by generative AI? Use a value-driven lens and avoid trying to generatively automate everything at once.
Oliver Wyman emphasizes working “from specific insurance problems backward”, not from technology forward. EY’s guidance echoes this: insurers should start with quick-win use cases, then scale.
Step 2: Pilot, Evaluate, Scale
Build a small pilot in a controlled domain (e.g. auto claims, routine underwriting). Evaluate accuracy, timeliness, user acceptance, risk of hallucination, and compliance. Once validated, scale to broader lines, geographies, or adjacent functions.
Step 3: Establish Infrastructure, Governance, and Skills
- Data & infrastructure: Build pipelines, feature stores, secure model deployment, APIs, and version control
- Governance & oversight: Create human-in-the-loop frameworks, audit trails, bias detection, and explainability
- Skills & culture: Train underwriters, claims agents, legal/compliance teams; embed AI awareness
- Feedback loops & iteration: Monitor performance metrics, correct drift, retrain models, and continuously improve
These three steps help insurers transition cautiously but purposefully toward confident AI adoption.
5. Challenges and Considerations
Even as AI holds promise, insurers must navigate several risks and constraints.
Model Hallucination & Accuracy
Generative AI can generate plausible but incorrect statements (“hallucinations”). In insurance, such errors are unacceptable. It’s essential to wrap LLMs with retrieval systems, fact-checking, or human validation layers.
Bias, Fairness & Transparency
If training data carries biases (e.g. socio-economic, gender, location), AI may perpetuate unfair pricing or exclusionary underwriting. A recent academic survey by Frederik Zuiderveen Borgesius (2025) on discrimination in AI insurance practices emphasizes consumers find opaque or unwarranted feature usage unfair.
Compliance, Legal & Regulatory Risk
Regulators in different jurisdictions are still crafting frameworks around AI usage, data protection, and model accountability. Guardrails and explainability are vital. Regulators may demand why a model made a decision. Oliver Wyman warns that regulation must evolve alongside AI deployment.
Integration & Legacy Systems
Many insurers use legacy core systems, siloed data, and rigid architectures. Integrating AI into these environments with low latency, secure access, and scalability is a major technical hurdle.
Change Management & Human Acceptance
Staff may resist AI intervention, fearing job displacement or losing control. Clear roles, transparent oversight, and training are critical to alleviate fears and fostering collaboration.
Liability & Auditability
Who is liable if an AI suggestion leads to incorrect underwriting or a claim denial? Insurers must define accountability, log model versions, and maintain audit trails.
Adversarial Risks & Robustness
Generative systems can be vulnerable to adversarial inputs (e.g. crafted prompts to trick models). Insurance AI must be resilient to such attacks (Elisa Luciano et al, 2023). Successfully navigating these challenges is essential for sustainable generative AI deployment in insurance.
Conclusion
Generative AI offers insurers an unprecedented lever: the ability to automate writing, reasoning, and content tasks across underwriting, claims, product design, and customer engagement. But the power of AI must be harnessed carefully with strategy, governance, human oversight, and prioritized deployment.
To transform from AI pilot projects to enterprise value engines, insurers should:
- Define focused use cases tied to business value
- Run pilots, learn, validate, then scale
- Build the data infrastructure, governance, and culture for responsible adoption
If you represent an insurance company seeking to harness generative AI (whether building narrative pipelines, modernizing underwriting, or embedding conversational agents), Verysell AI is ready to partner with you. We bring expertise in:
- Generative model integration
- Insurance domain knowledge
- Governance, audit, and compliance frameworks
- Scalable data & deployment architecture
- Human-AI design and training
Contact Verysell AI today to unlock how AI can become your strategic competitive advantage in the insurance industry.