Manufacturing 4.0 is the next evolution in industrial development, built on the foundation of Industry 4.0, where advanced technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and big data are redefining how factories operate. In this era, smart factories are more connected, agile, and data-driven, allowing businesses to optimize their operations and deliver higher quality products at lower costs. Let’s dive deeper into how AI is reshaping manufacturing automation with Verysell AI!
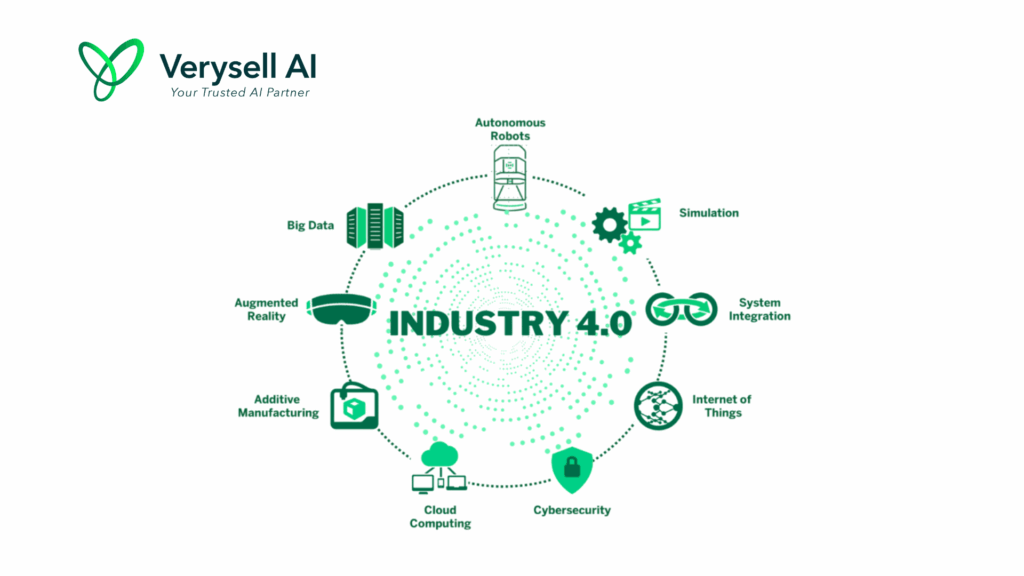
1. AI in Manufacturing 4.0
AI is at the core of this transformation, revolutionizing manufacturing processes and enabling smarter, more efficient, and flexible production systems (Peter 2025). As manufacturers move from traditional, manual-driven approaches to more automated and data-driven models, AI allows for significant advancements in every stage of the production process. At the heart of AI’s role in Manufacturing 4.0 is its ability to analyse vast amounts of data generated by connected machines and sensors. Rather than replacing human works, AI in manufacturing industries offers solutions for quality control, analytics, predictive maintenance, automation, and more.
>> Click here to read and explore more AI in manufacturing use cases and benefits!
2. Predictive Maintenance: Reducing Downtime
One of the most valuable applications of AI in smart factories is predictive maintenance. Traditionally, factories relied on scheduled maintenance, which meant that machinery was either repaired on a regular schedule or only after a failure occurred. Both approaches often led to costly downtime, as machines could break down unexpectedly, halting production.

AI changes this by using machine learning algorithms to analyze data from sensors embedded in equipment (Neural Concept, 2025). By continuously monitoring parameters like temperature, vibration, and pressure, AI can detect anomalies that may indicate an impending failure. These insights allow maintenance teams to intervene before a problem occurs, preventing unplanned downtime and optimizing the maintenance schedule.
For example, AI-powered predictive maintenance has been successfully implemented in industries such as automotive manufacturing, where machines are under constant pressure to operate at peak efficiency. By anticipating breakdowns before they happen, manufacturers can save money on emergency repairs, reduce the risk of production delays, and improve overall equipment lifespan.
3. Quality Control: Enhancing Precision and Accuracy
In any manufacturing process, maintaining consistent product quality is critical. AI helps improve quality control by enhancing precision and reducing human error. Advanced computer vision systems powered by AI can automatically inspect products at various stages of production. These systems use deep learning algorithms to identify defects, surface imperfections, or deviations from design specifications.

For instance, in the semiconductor manufacturing industry, AI-driven inspection systems can detect even the most minute flaws that may be invisible to the human eye. This level of accuracy ensures that only high-quality products make it to the final stages of production, while defective units are identified and discarded early in the process, saving time and resources.
Additionally, AI allows for continuous monitoring of production lines, enabling real-time adjustments to processes. If quality issues arise, the system can immediately alert operators, who can then adjust parameters to prevent further defects from occurring. This continuous feedback loop helps manufacturers maintain high standards and deliver superior products to customers.
4. Automation and Robotics: Enhancing Flexibility
AI-driven robotics are another crucial component of manufacturing automation in Industry 4.0. Robots equipped with AI are capable of performing complex tasks such as assembly, packaging, and even quality inspections with precision and speed. Unlike traditional robots, which follow pre-programmed instructions, AI-powered robots can learn from experience, adapt to new tasks, and make decisions based on data input.

For example, in automotive manufacturing, robots powered by AI are used to assemble intricate components like engines or chassis. These robots can adjust their movements and operations based on real-time feedback from sensors, ensuring that each component is assembled with high accuracy. This flexibility significantly reduces the need for human intervention, freeing up workers to focus on higher-level tasks.
Moreover, AI-enhanced robotics allow for greater customization in manufacturing processes. In industries like electronics and consumer goods, where customer demand often changes rapidly, manufacturers can quickly reconfigure robots to produce different products without major downtime or retooling. This adaptability is critical in today’s fast-paced manufacturing environment, where speed and flexibility are key to staying competitive.
5. Supply Chain Optimisation: Streamlining Operations
AI also plays a pivotal role in optimizing the entire supply chain process, from procurement to delivery. By analyzing historical data and real-time information from sensors, AI can forecast demand, track inventory levels, and optimize logistics routes to reduce delays and inefficiencies.

For example, AI algorithms can predict which parts will be needed in the production process and ensure that they are ordered and delivered on time. AI can also optimize production schedules to ensure that resources are used efficiently and production capacity is maximised. Moreover, AI can help manufacturers reduce waste by optimizing raw material usage. By predicting the exact amount of materials required for production, AI minimizes overstocking and understocking issues, leading to cost savings and a more sustainable operation.
In addition, AI-powered systems can improve the traceability of products along the supply chain. By tracking components from their origin to the final product, AI ensures transparency and helps meet regulatory requirements in industries such as pharmaceuticals, where precise traceability is a legal necessity.
6. Energy Management: Driving Sustainability
As manufacturing processes become increasingly energy-intensive, sustainability has become a critical concern. AI can help manufacturers optimize energy consumption by analyzing data on energy usage and recommending more efficient production practices. AI algorithms can monitor energy consumption across different parts of the manufacturing process and suggest improvements to reduce waste.

For example, AI can determine the optimal time for machines to operate based on electricity price fluctuations, or it can adjust the speed of production lines to conserve energy during periods of low demand. By integrating AI into energy management, smart factories can significantly reduce their carbon footprint while saving on energy costs. This not only benefits the environment but also helps companies stay compliant with increasingly strict environmental regulations.
7. Enhanced Decision Making: Data-Driven Insights
AI allows manufacturers to collect vast amounts of data throughout the production process. This data is then analyzed to provide valuable insights that inform decision-making. By leveraging machine learning algorithms, AI systems can identify patterns and trends that might be difficult for human operators to spot. For example, AI can analyze customer feedback, market conditions, and production data to predict trends and adjust production strategies accordingly. This enables manufacturers to respond to changing market demands quickly, allowing for more agile decision-making and competitive advantage.

Additionally, AI-powered systems can help managers make more informed decisions by providing them with real-time data visualizations and predictive analytics. By having access to accurate and up-to-date information, decision-makers can make choices that optimize production, reduce costs, and improve overall performance.
Why You Should Implement AI in Smart Factory Automation?
The best role of AI in Manufacturing 4.0 is its ability to transform factories into highly efficient, flexible, and autonomous operations. From predictive maintenance and quality control to energy management and supply chain optimization, AI is revolutionizing every aspect of manufacturing. As companies continue to embrace AI technologies, smart factories will drive the next wave of industrial innovation, offering manufacturers a competitive edge in an increasingly complex global market.
In the era of Manufacturing 4.0, AI is not just a tool for automation; it’s a catalyst for innovation, enabling businesses to adopt advanced manufacturing techniques like additive manufacturing, robotic process automation, and predictive analytics. By integrating AI into their operations, manufacturers can unlock new possibilities for reducing costs, increasing throughput, and maintaining consistent product quality. This transformation is essential for companies aiming to thrive in the fast-paced, interconnected world of modern manufacturing.


