Retail predictive analytics definition
Retail predictive analytics involves gathering data on retail operations and utilizing it to enhance a business’s understanding of customers, inform decisions regarding products and marketing, and ultimately discover ways to improve the business. Effective analytics have become essential for contemporary retailers. This blog post delves into the various techniques and application areas of retail analytics.

How retail predictive analysis works
Predictive analytics relies heavily on data, but in a business context, having usable data isn’t always guaranteed. Therefore, the first step in retail predictive analytics is to identify the questions you want to address and determine the necessary data to answer them. This data can be categorized into two types: readily available data and data that requires additional effort to collect.
1. Readily Available Data
This includes information such as sales figures, transaction details, and online orders, often referred to as “digital exhaust” since it’s generated through regular business operations. You may already have this data well-organized through your existing sales, customer, and inventory management systems, or you might need minor adjustments to ensure its usefulness for analytics.
2. Data Requiring Extra Effort
This type of data necessitates additional efforts to collect, such as customer satisfaction surveys. Creating and administering these surveys is essential to gather the insights needed for analysis. The specific data collected should align with the questions you wish to answer, a relationship explored later in this article. There are generally three types of predictive analytics tasks to perform on it: description, extrapolation, and inference:
- Description: The goal of description is to summarize and present data in a way that enhances decision-makers’ understanding of operations. Data analysts generate useful summaries and visualizations, making raw data more accessible. This stage often includes basic statistical methods, such as averages and growth rates, and may involve dashboards for real-time updates of key performance indicators (KPIs). Descriptive analytics can answer essential questions about sales, busy months, and regional growth trends.
- Extrapolation: In retail, its analytics focuses on forecasting future data trends using current and historical information. By applying statistical techniques, such as regression analysis, analysts can identify patterns and project future business conditions. This practice is crucial for demand and inventory forecasting, allowing businesses to prepare for upcoming scenarios based on insights from historical data.
- Inference: It is a complex task that often requires specialized statistical expertise. It involves exploring causal relationships, such as determining how much factor X influences outcome Y, typically using experimental data like A/B testing. For example, when analyzing the impact of a promotional sale on sales and profits, it’s essential to isolate the promotion’s effect from other influencing factors, such as market trends or competitor actions.
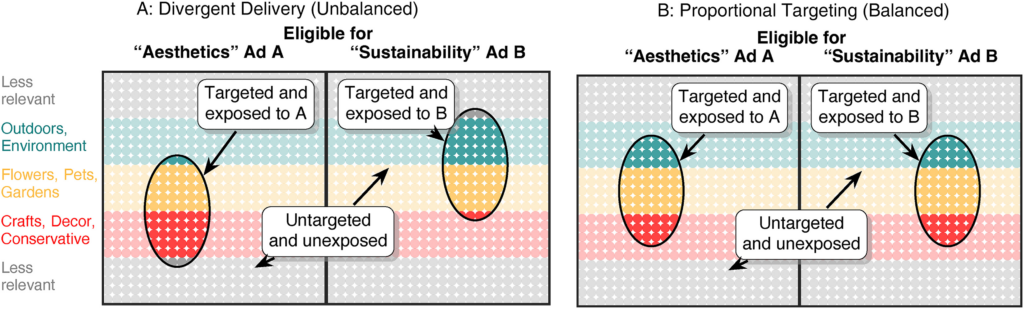
Mixes of Targeted Users in A/B Tests With and Without Divergent Delivery (Source: Michael Braun and Eric M. Schwartz)
Benefits of retail predictive analytics
1. Increased Sales
The primary objective for most retailers embarking on an analytics journey is to boost sales. Effective retail analytics helps retailers reinforce successful strategies, identify and replace underperforming tactics, and determine the optimal timing and audience for marketing messages and promotions. Nearly all effective applications of retail analytics contribute directly or indirectly to sales growth.
>> Read more: Top 7 AI in the retail trends in 2025

2. Improved Profitability
In the long term, companies aim to optimize profitability rather than just sales figures. By enhancing the collection and analysis of sales data in conjunction with margin data, businesses can adjust their product offerings to focus on higher-profit transactions. For instance, a popular but low-margin entry-level product might initially seem unimportant, but analysis could reveal that its sales drive overall profitability by attracting customers and fostering loyalty that leads to future upsells.

3. Refined Marketing Targeting
Robust data collection and analysis can significantly improve the effectiveness of marketing campaigns. Retailers may discover that certain campaigns resonate better with specific customer segments, perform differently in various regions, or yield better results in certain seasons. For example, a retailer selling organization products might find that older customers respond best to spring promotions, while middle-aged customers are more receptive to offers at the end of summer as they prepare for back-to-school shopping.

Campaign effectiveness analysis: From Data to Insights (Source: Blue Atlas)
4. Enhanced Customer Experience and Loyalty
Modern technology offers numerous ways to measure and enhance customer experience, from simulating customer flows in stores to analyzing data from cameras that track where customers linger. Different businesses will have varying metrics for success; for instance, a bar may aim to create an inviting atmosphere for customers to linger, while a coffee shop prioritizes quick service for morning rushes. Ultimately, providing superior customer interactions fosters loyalty, repeat business, positive reviews, and referrals.
5. Better Staff Scheduling
One of the significant challenges for physical retail locations is accurately predicting staffing needs for specific days and times. Businesses must avoid having too many sales staff without customers or a small team overwhelmed by high traffic. Retail predictive analytics can help forecast busy periods, leading to better alignment of staffing levels with customer demand and providing employees with more predictable schedules. This results in fewer lost sales from understaffed stores, reduced costs from overstaffing, and improved employee satisfaction with more stable work hours.
Conclusion
By this point it should be clear that retail predictive analytics is impossible to do by hand or with spreadsheets. With some services from Verysell AI, it will help store usefully and running retail predictive analytics for a midsize or larger retailer. Businesses need software capable of drilling down to individual locations and even transactions. Contact us to get more information!


