AI in manufacturing leading the charge toward smarter, faster, and more resilient industrial processes when the Fourth Industrial Revolution has firmly taken root. As artificial intelligence continues to evolve, its profound influence is not restricted to a single domain but extends across multiple manufacturing sectors, redefining the very fabric of production.
This blog post explores how AI is reshaping five critical manufacturing industries: automotive, electronics, pharmaceutical, aerospace, and consumer goods.
Read more: Unlocking the power of AI in the manufacturing industry
1. Automotive Manufacturing: Accelerating Smart Production
The automotive industry stands at the forefront of AI-driven transformation. AI algorithms are now integral to optimizing assembly lines, predictive maintenance, and autonomous quality inspections.
In the automotive industry, AI in manufacturing is transforming operations through several key applications. Predictive maintenance systems leverage AI models to analyze real-time machine data, anticipating failures before they occur and thereby minimizing downtime and maintenance costs. Simultaneously, computer vision technologies enable visual quality inspections that detect microscopic defects, achieving precision beyond human capabilities. Additionally, AI-driven supply chain optimization improves demand forecasting, supplier coordination, and logistics management, fostering greater agility and cost-efficiency.
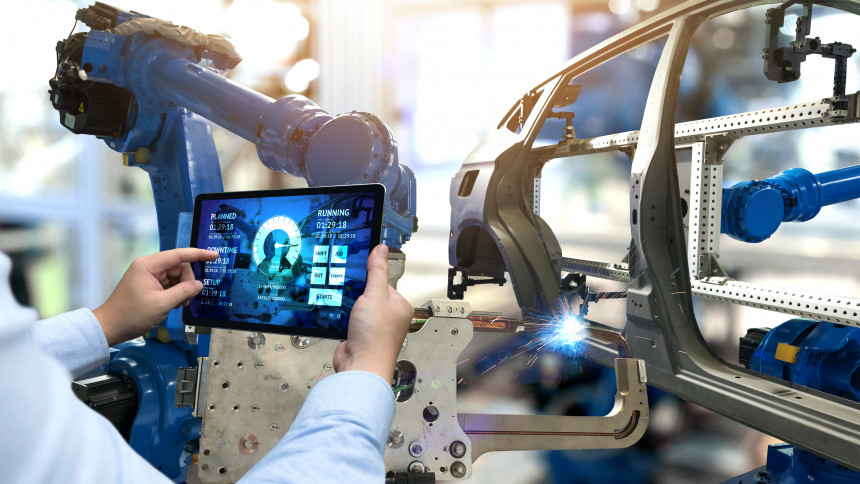

Therefore, the tangible benefits are substantial: manufacturers like Tesla and BMW have reported efficiency improvements ranging from 20% to 30% through AI-driven initiatives, leading to lower warranty claims and enhanced customer satisfaction (Taylor, 2025, BMW Group, 2025).
2. Electronics Manufacturing: Precision and Agility at Scale
The electronics sector, with its intricate and high-precision demands, has embraced AI in manufacturing to handle the complexity of modern devices. AI in manufacturing involves using technology to automate complex tasks and unearthing previously unknown patterns in manufacturing processes or workflows.
In the electronics industry, AI in manufacturing is driving remarkable advances across production processes. Robotic process automation (RPA) now manages intricate tasks such as Printed Circuit Board (PCB) assembly with enhanced speed and reduced error rates, significantly improving operational efficiency. Concurrently, AI-powered anomaly detection systems proactively identify defects during production, safeguarding against costly recalls and ensuring consistent product quality. Furthermore, machine learning algorithms predict yield outcomes by analyzing real-time production data, enabling manufacturers to make timely, data-driven adjustments.
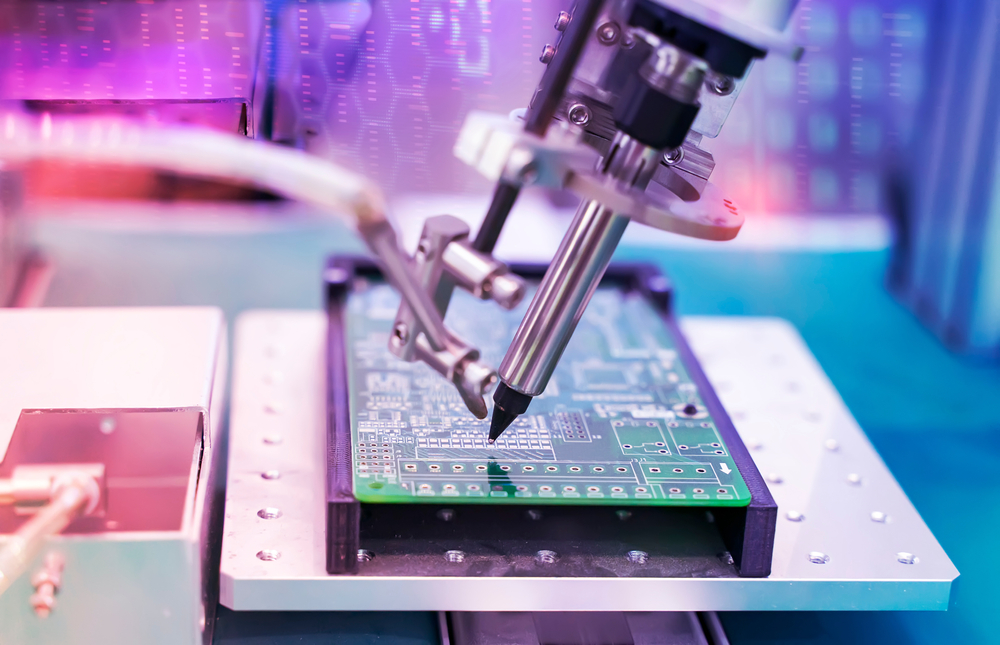

As a result, leading companies such as Samsung and Foxconn leverage AI to enhance production yields by over 15%, minimize waste, and drastically shorten time-to-market for new electronics (Puhuja, 2025). Moreover, Foxconn has embraced AI as a core pillar of its future strategy. The company is leveraging AI to enhance manufacturing efficiency through smart factories and automation.
AI use cases in Foxcom. Firstly, leveraging algorithm-driven automation and digital twin technology to optimize workflow, lower energy consumption, and improve profitability. Secondly, AI-powered quality inspection to enhance efficiency is deploying deep learning algorithms for quality inspection to boost accuracy, reduce defects, and lower rework costs.
3. Pharmaceutical Manufacturing: Ensuring Safety and Efficiency
Pharmaceutical manufacturing demands the highest levels of precision, regulation, and consistency. Here, AI in manufacturing plays a pivotal role in achieving compliance, enhancing drug quality, and accelerating time-to-market.
In the pharmaceutical industry, AI in manufacturing is ushering in a new era of precision, efficiency, and compliance. By 2025, AI spending in the pharmaceutical industry is expected to hit $3 billion, reflecting a surge in its adoption to reduce the hefty time and costs associated with drug development. Alliances focused on AI-driven drug discovery have skyrocketed from just 10 collaborations in 2015 to 105 by 2021 demonstrating its growing influence.
Process Analytical Technology (PAT) empowered by AI continuously monitors and adjusts manufacturing parameters in real time, ensuring the production of consistently high-quality drugs. Simultaneously, AI accelerates the drug discovery process by predicting molecular interactions and optimizing the selection of candidate compounds, significantly reducing the time and cost associated with bringing new medicines to market. Moreover, AI strengthens supply chain integrity by enhancing visibility and traceability, which is vital for regulatory compliance and effective risk management in this highly regulated sector.

Companies like Pfizer and Novartis use AI to cut drug development times by 10-20%, enabling faster responses to emerging health crises and reducing overall production costs (Coherent Solutions, 2025). For example, in the COVID 19 pandemic, Pfizer leveraged AI drug discovery’s potential despite the low 12% success rate of drugs in clinical trials.
4. Aerospace Manufacturing: Pioneering the Future of Engineering
The aerospace industry, synonymous with innovation and engineering excellence, has integrated AI in manufacturing to meet its exacting standards.
In the aerospace industry, AI in manufacturing is propelling engineering innovation to new heights. Through additive manufacturing, AI optimizes 3D printing parameters, enhancing material usage efficiency and boosting part performance, which is crucial for the lightweight and durability requirements of aerospace components. Predictive analytics further strengthens operational safety by forecasting the wear and potential failure of critical parts, allowing maintenance teams to intervene proactively and minimize downtime. Additionally, autonomous production cells powered by AI orchestrate entire manufacturing workflows with minimal human intervention, ensuring consistent quality, enhanced precision, and significant operational efficiency in an industry where failure is not an option.

Airbus has leveraged AI to significantly improve its manufacturing processes. Through the implementation of AI-enhanced predictive maintenance, the company has successfully reduced manufacturing defects by more than 15%. This improvement has translated into substantial annual savings, amounting to millions of dollars. The integration of AI-driven quality assurance systems has been a key factor in enhancing operational efficiency and product quality (SmartDev, 2024).
5. Consumer Goods Manufacturing: Enhancing Personalization and Speed
In the consumer goods industry, AI in manufacturing is revolutionizing production processes by enabling more personalized, efficient, and sustainable practices. Through mass customization, AI analyzes consumer data to allow for on-demand, tailored production of items ranging from sneakers to skincare products, meeting the unique preferences of individual customers. Additionally, AI-driven analytics improve demand forecasting, helping companies better plan production and reduce the risks of overproduction and waste. Furthermore, machine learning models are optimizing resource consumption, making production lines more sustainable by minimizing energy use, water consumption, and material waste, thus significantly reducing the environmental footprint of manufacturing operations.

Nike is leveraging AI to offer highly personalized products at a scale, catering to the unique preferences of individual customers. By using AI-driven data analysis, these companies can tailor their offerings, improving customer satisfaction and loyalty. This results in significant reductions in carbon emissions, helping these brands meet sustainability goals while maintaining efficiency and profitability.
The Challenges Ahead
Despite the numerous advantages, implementing AI in manufacturing comes with its set of challenges. The high initial costs of adopting advanced AI technologies can be a significant barrier, as organizations must invest heavily upfront. Additionally, there is a notable skills gap, with a shortage of workers proficient in both manufacturing processes and AI technologies, which hampers effective implementation. Managing and securing the vast amounts of data generated by AI systems is another complex issue, requiring robust infrastructure and cybersecurity measures.
Furthermore, integrating AI into legacy manufacturing systems can be technically demanding, often requiring extensive modifications. However, companies that successfully navigate these obstacles are positioned to gain substantial long-term benefits, including enhanced efficiency, reduced costs, and a competitive edge in their respective markets.
Conclusion
AI in manufacturing is no longer a futuristic concept; it is a current reality driving profound transformation across multiple industries. Automotive, electronics, pharmaceuticals, aerospace, and consumer goods sectors are witnessing unprecedented innovation, operational efficiency, and customer-centric production models.
As AI continues to mature, the manufacturers who embrace its potential today will lead the industries of tomorrow, setting new benchmarks for excellence, sustainability, and agility. Are you excited to explore AI in manufacturing soon? Contact us today to discover how AI helps optimize your business.