AI in manufacturing spans a wide spectrum, from the intricacies of supply chain management to the sophisticated challenges of optimizing product design. By harnessing advanced algorithms and machine learning, manufacturers can gain real-time insights into inventory levels, demand forecasting, and logistics, thus enhancing operational efficiency and reducing costs. Moreover, AI enables predictive maintenance, allowing for the early detection of equipment issues before they lead to costly downtime. In product design, AI-driven simulations and generative design tools facilitate rapid prototyping and customization, enabling manufacturers to meet specific customer needs with unprecedented speed and precision. In this blog post, we will explore top 10 best benefits and use cases of AI in manufacturing, what it involves, why it matters.
What is AI in Manufacturing?
Modern manufacturers leverage AI to automate tasks and support workers throughout the entire manufacturing process, from initial product design to assembly and post-production quality control (HSO, 2023). By analyzing vast datasets to identify patterns and predict outcomes more quickly than even the most skilled human analysts, AI enhances visibility, minimizes workflow redundancies, and optimizes material usage within supply chains.

AI’s impact goes beyond mere data analysis; for instance, AI-driven robots can operate autonomously or collaborate with human workers on the shop floor, identifying and reporting errors or defects in real time. As AI technology continues to advance, fueled by machine learning (ML) algorithms, manufacturers will experience increased productivity and reduced costs across all aspects of their operations.
AI in Manufacturing Benefits
According to the survey of Manufacturing Leadership Council (2023), in every instance, at least 70% of respondents said AI would have a high or moderate benefit. Twenty-eight percent of respondents report that they are currently operationalizing AI projects, particularly in manufacturing and production, as well as inventory management. In fact, over one-third of companies in each of these categories are concentrating a significant portion of their AI efforts there. By understanding the importance of the five benefits below, manufacturing leaders can better track AI’s impact.
1. Improve Maintenance and Operations
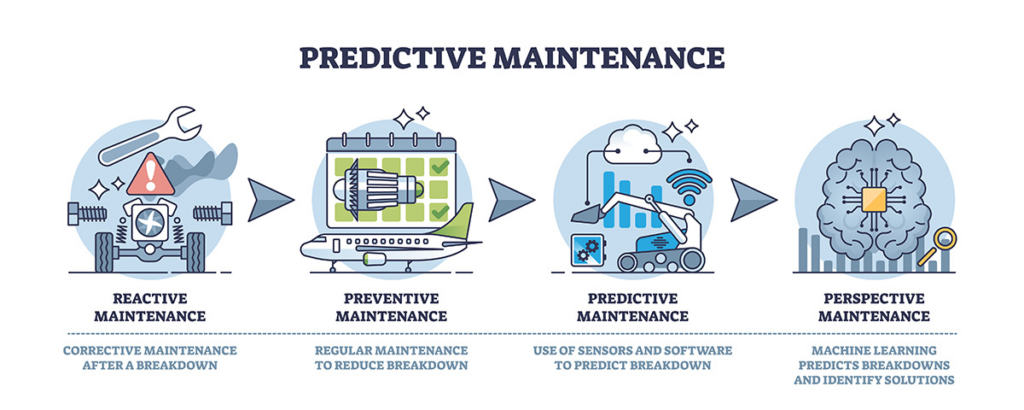
AI and machine learning (ML) can significantly enhance maintenance scheduling and repair processes. This predictive maintenance approach allows businesses to anticipate potential failures before they occur. AI systems continuously monitor equipment conditions, identifying anomalies such as unusual vibrations, temperature spikes, or other indicators of potential failure (WorkTrek, 2025). By addressing these issues proactively, companies can avoid unplanned downtime, which can be costly and disruptive to operations. Moreover, with AI’s ability to predict when maintenance and operations is needed, companies can optimize their workforce and inventory management (SmartDev, 2024). This ensures that the right parts and personnel are available when required, reducing waste and improving overall efficiency.
2. Supply Chain and Inventory Management
AI is transforming supply chain and inventory management in manufacturing by enhancing visibility, efficiency, and responsiveness. By analyzing vast amounts of data from various sources, including sales forecasts, market trends, and supplier performance, AI algorithms can predict demand more accurately, allowing manufacturers to optimize inventory levels and reduce excess stock. The integration of AI in supply chain management not only enhances operational efficiency but also enables manufacturers to respond swiftly to changing market demands, ultimately driving competitiveness in a dynamic industry landscape.
>> Read more: Automated Order Processing and Inventory Management in Retail

3. Innovation and Competitive Advantage
AI enhances the prototyping process by enabling rapid iteration. Traditional prototyping can take weeks or months, but AI tools can create digital prototypes in a fraction of the time. For instance, using AI-driven 3D printing technologies, manufacturers can produce functional prototypes within hours, allowing for quicker testing and feedback cycles (Rasu, 2023).
Moreover, this AI-driven approach allows designers to input specific parameters—such as materials, weight constraints, and manufacturing methods—and then generates multiple design alternatives that meet those criteria. This process can lead to innovative solutions that a human designer might not consider, resulting in optimized products that are lighter, stronger, and more cost-effective.
4. Cost Efficiency and Business Value
AI-driven automation streamlines repetitive processes such as assembly, packaging, and quality checks. By replacing manual labor with automated systems, companies can significantly reduce labor costs. For instance, a study by McKinsey found that automation can cut labor costs in manufacturing by up to 30% (McKinsey, 2019). Besides, applying AI-driven forecasting to supply chain management, can reduce errors by between 20 and 50 percent (McKinsey, 2022). Utilizing AI for predictive analytics allows manufacturers to forecast demand and adjust production schedules accordingly. This minimizes overproduction and underutilization of resources.
>> Read more: The Future of Smart Factories: Integrating AI and IoT
Besides, AI algorithms optimize material usage by analyzing production processes and identifying areas where waste occurs. It can analyze production data to identify inefficiencies, optimize resource allocation, and streamline workflows. AI systems can analyze production data in real time to detect defects earlier in the manufacturing process. For example, using machine vision systems, manufacturers can achieve defect detection rates of over 95%, reducing the costs associated with rework and scrap materials (Aciinfotech, 2024). Overall, integrating AI into manufacturing not only drives innovation but also significantly lowers operational costs, resulting in a leaner, more efficient production environment.
>> Read more: 4 AI in the Retail Industry Best Cost Reduction Suggestions
5. Safety and Compliance
Collaborative robots, or cobots, equipped with artificial intelligence are revolutionizing workplace safety by performing strenuous or hazardous tasks alongside human workers (Hansen, 2024). Unlike traditional industrial robots that operate in isolation, cobots are designed to work collaboratively, sharing the workspace with humans. This synergy allows for a division of labor where cobots can take on physically demanding jobs, reducing the risk of injury for human employees. For instance, in assembly lines, cobots can lift heavy components, allowing human workers to focus on more precise and intricate tasks.
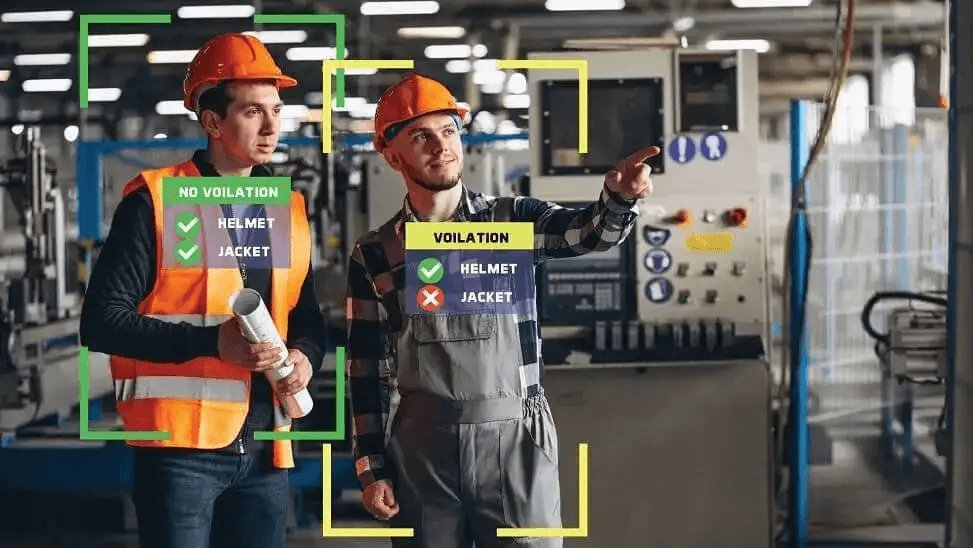

In addition to cobots, smart systems and augmented reality (AR)-guided workflows further enhance safety and efficiency in manufacturing settings. These technologies provide real-time guidance and support for workers, ensuring they perform tasks with precision and confidence. AR systems can overlay instructions onto the physical environment, helping employees visualize complex assembly processes or safety protocols.
Conclusion
The integration of AI in manufacturing is not just a trend; it represents a fundamental shift in how industries operate, innovate, and compete. From enhancing maintenance and supply chain efficiencies to fostering rapid prototyping and improving workplace safety, AI offers a multitude of benefits that can significantly transform manufacturing processes. These advancements not only lead to cost reductions but also empower manufacturers to respond swiftly to market changes and customer demands. As companies continue to harness the power of AI, they will not only improve their operational efficiencies but also position themselves for sustained growth and innovation in an increasingly competitive landscape. Embracing AI technology is essential for manufacturers aiming to thrive in the future of smart manufacturing.


